How Do I Find The Registered Owner Of A Domain Name
What is Domain Name System or DNS?
A Domain Name Organisation (DNS) showtime emerged in the early 1980s. It represents a organisation of interconnected servers that shop registered domain names and Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
As the Internet grew, information technology became an unavoidable function of online interaction. The majority of internet users are not fifty-fifty aware of DNS and the huge favor it does us. Without DNS, you cannot access any website past typing a URL in your browser.
Computers talk to each other using IP addresses. Since humans cannot memorize thousands of strings of numbers, nosotros have to utilise domain names instead of IP addresses. It is much easier to remember to blazon phoenixnap.com into your browser than 198.24.170.115.
When y'all want to visit a website, your computer needs to know the verbal IP address; it does non care virtually the domain proper name.
DNS keeps the record of all domain names and the associated IP addresses. When y'all type in a URL in your browser, DNS resolves the domain name into an IP accost.
In other words, DNS is a service that maps domain names to corresponding IP addresses.
How Does DNS Piece of work?
DNS is at the core of the Internet we use today.
The latest report shows there were 342.four 1000000 domain names in the third quarter of 2018 and we would accept been lost without DNS to resolve them into IP address.
When y'all want to call someone using your jail cell phone, information technology is highly unlikely you punch in the exact phone number. Instead, you load the contact list and search using the person'due south proper noun. DNS does the same thing when you want to load a website.
Resolving a domain proper noun or a hostname goes through several different phases.
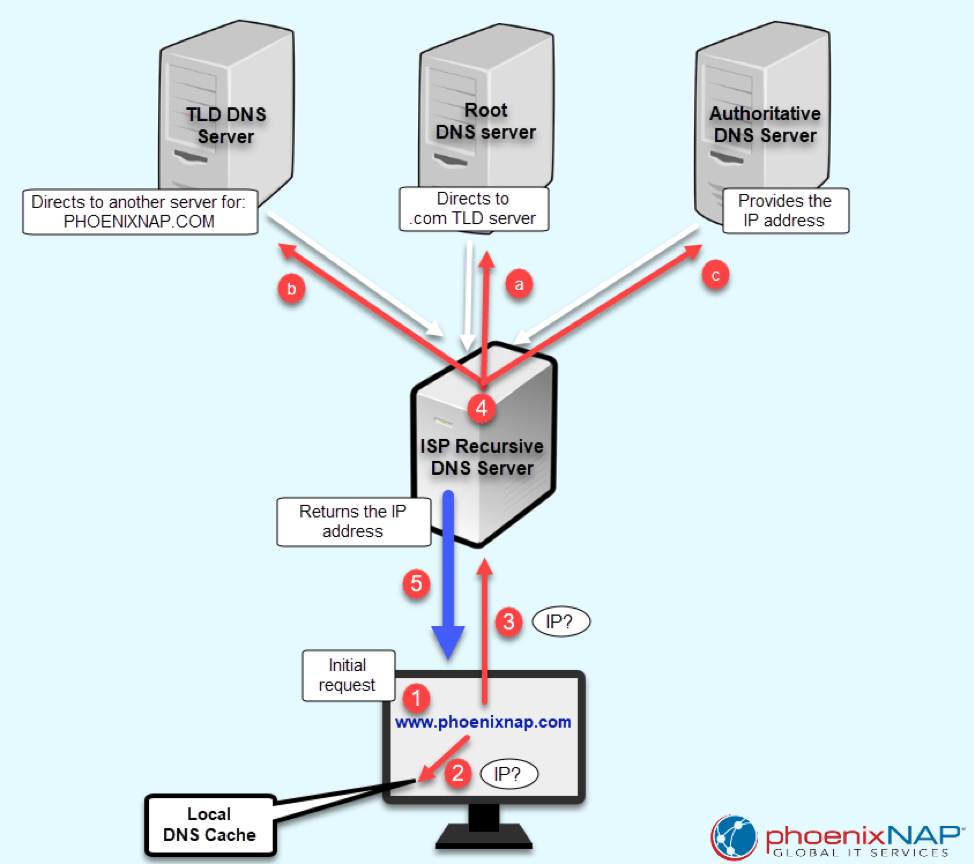
On some occasions, DNS resolving is a one-step procedure, while on the other information technology involves contacting multiple DNS servers. The diagram below shows the necessary steps in this procedure and does non take into account the browser cache.
Why is DNS Cached?
DNS caching or flushing is an effective mode to reduce potential DNS queries towards DNS nameservers. This speeds upwardly the domain name resolving procedure.
Caching happens at multiple locations. This includes your computer, sometimes routers, while all DNS servers take their own databases with cached data.
Step ane – Send a Request to Resolve a Domain Proper name
When y'all type www.phoenixnap.com into a browser, in order to load the webpage, your reckoner asks for the IP address. Computers do not know in advance where they tin find the necessary data, so they try searching through the DNS enshroud and whatever available external source.
Stride 2 – Search for an IP Locally
Earlier going externally, your computer loads the local DNS cache database to run across if you already requested the IP for that domain name. Every computer has a temporary enshroud with the most recent DNS requests and attempts to connect to online sources.
When the DNS cache has the IP data for the website that you are trying to connect to, the page loads immediately. DNS cache expedites this lookup process since the computer contains the information information technology needs and does not have to forward the request to your ISP.
Step 3 – Contact ISP and its Recursive DNS Server to Resolve a Domain Name
A reckoner'south local DNS cache database does non always contain the necessary information to resolve a domain proper noun. In that instance, the request goes further to your Isp (ISP) and its DNS server.
In one case information technology gets a request, the resolver looks in its records to provide the correct IP address. When the necessary information is nowadays in the Internet access provider server's buried records, the reckoner gets dorsum the IP and connects to the website. If Internet service provider's recursive DNS server cannot resolve the domain name, it contacts other DNS servers to provide the information dorsum to you. This is why we call them recursive servers. Every Internet Service Provider has at least a secondary DNS server setup to ensure maximum high availability of the service.
Step 4 – Ask Exterior DNS Servers to Provide an IP Accost
Isp DNS resolvers are configured to ask other DNS servers for correct IP address mapping until they can provide data back to the requester. These are iterative DNS queries.
When a DNS client sends such a asking, the first responding server does non provide the needed IP accost. Instead, it directs the request to another server that is lower in the DNS bureaucracy, and that ane to another until the IP address is fully resolved. At that place are a few stops in this process.
- Root domain nameservers. Root servers themselves do not map IP addresses to domain names. Instead, they hold the information about all top-level domain (TLD) nameservers and point to their location. TLD is the rightmost section of a domain name, for case, .com in
phoenixnap.comor .org inwww.technology.org. Root servers are critical since they are the start stop for all DNS lookup requests. - TLD nameservers. These servers comprise the data for second-level domains, such as 'phoenixnap' in
phoenixnap.com. Previously, the root server pointed to the location of the TLD server. Then, the TLD server needs to direct the request toward the server that contains the necessary data for the website we are trying to reach. - Authoritative nameserver. Authoritative servers are the final destination for DNS lookup requests. They provide the website's IP address back to the recursive DNS servers. If the site has subdomains, the local DNS server will keep sending requests to the authoritative server until information technology finally resolves the IP address.
Pace v – Receive the IP Address
In one case the Isp's recursive DNS server obtains the IP accost by sending multiple iterative DNS queries, it finally returns it to your reckoner. The record for this asking now stays cached on the hard bulldoze. The browser tin can and then fetch this IP from the cache and connect it to the website's server.
When we interruption it downwardly like this, the process of DNS lookup seems to take a long fourth dimension to consummate. In fact, it takes milliseconds, with maybe a few milliseconds more than if the DNS tape is not in the local cache. In both cases, users cannot tell the departure. This is a basic description of how DNS works, and it should give you an thought what goes on under the hood when you browse or send an email.
Conclusion
This article has explained what a Domain Proper name Arrangement is and how information technology works. It covered the essential DNS functions and what needs to happen earlier you tin connect to an online server using its domain name.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/what-is-domain-name-system-works
Posted by: phamlinto1944.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Do I Find The Registered Owner Of A Domain Name"
Post a Comment